The AV MBA | Cash Flow Management when Purchasing DVLED: A Case for Distribution
Payables are fairly predictable in the AV business. Most distributors and suppliers offer NET 30 terms to qualified resellers, and the clock starts ticking upon shipment. A common rumbling I’ve heard over the years is that end-users may be slower to pay due to terms set to ‘payable upon completion’ of the project. If you are an integrator who has been in the business for a while, I’m sure you have run into this scenario, but usually, this will not tie up your receivables for more than 30 to 60 days.
The arrival and increasing demand for DVLED technology has been a great boon for our industry as any new technology is. However, it carries some key distinctions when it comes to cash flow implications compared to typical, traditional AV products.
 First, the average sales price (ASP) for DVLED is comparatively higher than technology such as large format displays (LFD), projectors, and audio. This fact alone immediately has a greater impact on cash flow. Obviously, $10,000 is an easier balance to float for a couple of months than $100,000. So, it is crucial that the balance doesn’t sit on the books for too long and risks impeding an integrator’s ability to pay other scheduled bills.
First, the average sales price (ASP) for DVLED is comparatively higher than technology such as large format displays (LFD), projectors, and audio. This fact alone immediately has a greater impact on cash flow. Obviously, $10,000 is an easier balance to float for a couple of months than $100,000. So, it is crucial that the balance doesn’t sit on the books for too long and risks impeding an integrator’s ability to pay other scheduled bills.
Another key difference is the supply chain impact on lead time. Aside from All-In-One (AIO) packages, custom configured LED solutions—which make up the majority of the demand—are not readily available to be purchased from manufacturers or distributors. They must be prepared to order, manufactured overseas and shipped via ocean freight. In my experience, the typical lead time for direct shipping a DVLED wall from overseas is more than 100 days. Normally, from a cash flow perspective, this wouldn’t be a problem as the goods would be payable upon receiving or 30 days after receiving if you have credit terms.
However, DVLED is unique in that manufacturers have embraced a standard practice of 1) Requiring a deposit (usually around 30%) up front prior to production, and 2) start the billing clock upon leaving the dock.
All these factors add up and the result is that the integrator is forced to have cash out-of-pocket for a disproportionate amount of time. Thus, potentially disrupting future business.
Here is a breakdown:
Figure 1: Vendor Direct Purchase
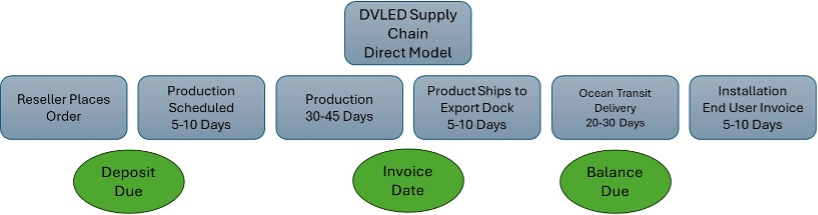
Figure 2: Distribution Purchase – Direct Ship from Overseas
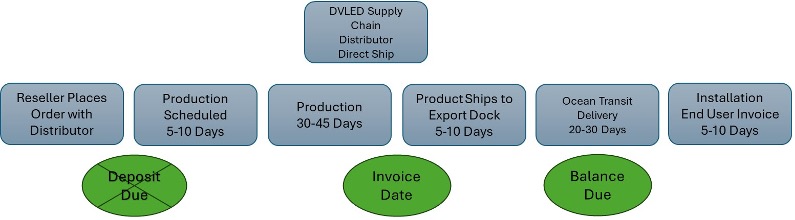
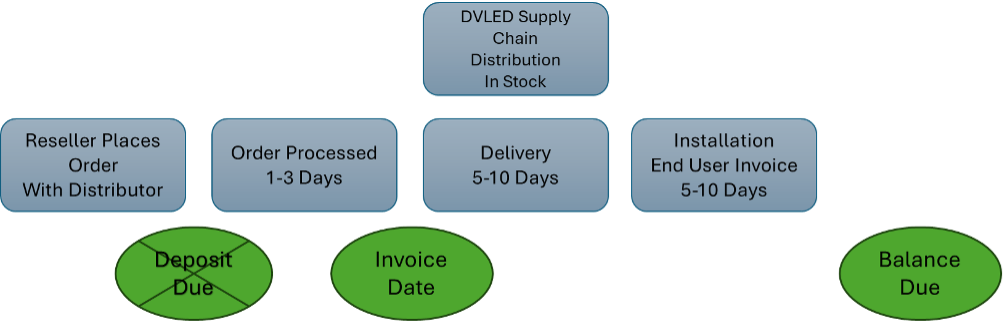
Figure 3: Distribution Purchase – Shipping from Domestic Stock
If you compare these cash flow charts, you will see that purchasing direct from a manufacturer (Figure 1) will have the most negative impact on cash flows, as a deposit is required upon placing the order, and the invoice will be generated upon shipping from the factory. This results in outlaying of a portion of cash up front on day one, thus tying up those funds for upwards of 100 days!!! When talking about DVLED projects, a $100,000 project is not uncommon, which would equate to a $30,000 deposit outlay.
When purchasing through distribution (Figure 2), the distributor is responsible for paying the deposit, thus, the reseller is not responsible for any up-front cash down. While invoicing will still begin at the time the order ships, often times, arrangements can be made between the reseller and distributor to assist in mitigating any negative cash flow impact if it is prohibitive to the completion of the project.
Finally, we see the benefits of purchasing DVLED from a distributor that has inventory available in stock. Frequently, this is the case when purchasing through Exertis Almo, as we are one of the only distributors in the U.S. dedicated to stocking both AIO and custom solutions in multiple sizes, configurations and pixel pitches. By purchasing products that are domestically available, the cash-flow impact is flipped, and the balance does not become due until well after a project’s completion in most cases.
Whether you buy through Exertis Almo or vendor direct, it’s important to approach DVLED purchases with eyes wide open, because as they say, Cash is King.

About the Author
Tom Keefe | CTS, DMC-D-4K, DSCE
Category Manager – dvLED
Supported Category: Direct View LED

 As I write this article, my truck is in the shop having new tires put on. Buying tires is one of my least favorite purchases of all time!!! Yet every few years I go through the same process. Gather my tire size information, check some tire websites, identify my needs in terms of performance (I live in Buffalo, NY, so a tire that performs well in the snow is a must!!!), establish my budget, read some reviews, select my top picks, shop prices, book the appointment.
As I write this article, my truck is in the shop having new tires put on. Buying tires is one of my least favorite purchases of all time!!! Yet every few years I go through the same process. Gather my tire size information, check some tire websites, identify my needs in terms of performance (I live in Buffalo, NY, so a tire that performs well in the snow is a must!!!), establish my budget, read some reviews, select my top picks, shop prices, book the appointment.
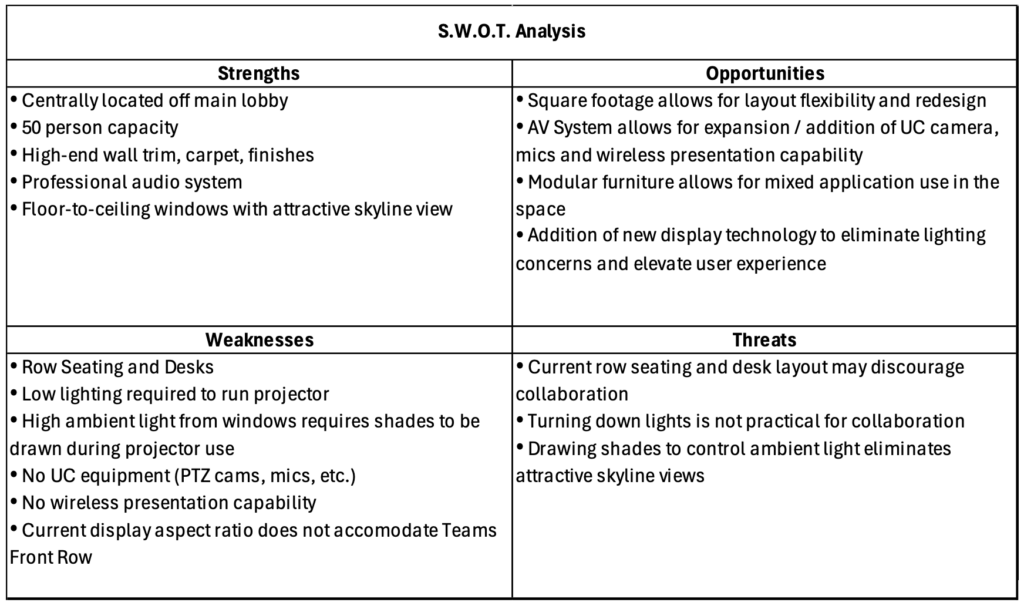
 Balancing these tradeoffs requires careful planning and consideration of the project’s specific needs and constraints. Conducting a feasibility study and involving all stakeholders in the planning process can help identify the best approach
Balancing these tradeoffs requires careful planning and consideration of the project’s specific needs and constraints. Conducting a feasibility study and involving all stakeholders in the planning process can help identify the best approach 
 Product
Product
 The first thing I did was to put together a SWOT analysis.
The first thing I did was to put together a SWOT analysis. When considering Price, I knew that we could not fetch the same price for this line that we would for a premium brand. I also knew that if we priced the product to be the lowest on the market, there would be no profit for the dealer and our product would be compared with cheap, inferior products that were not intended for professional use. Looking back at the newly defined product offer being a sales tool vs. a physical product, I looked at pricing in a similar way. Instead of a strategic price level—low, middle, high, etc.—it seemed to make more sense to again relate the price to the customer vs. the market. We would set a MAP (minimum advertised price) that was designed to deliver a significantly higher-than-average profit margin to our dealer. So, of course, the product had a price, but the focus was on dealer profit vs. end user cost.
When considering Price, I knew that we could not fetch the same price for this line that we would for a premium brand. I also knew that if we priced the product to be the lowest on the market, there would be no profit for the dealer and our product would be compared with cheap, inferior products that were not intended for professional use. Looking back at the newly defined product offer being a sales tool vs. a physical product, I looked at pricing in a similar way. Instead of a strategic price level—low, middle, high, etc.—it seemed to make more sense to again relate the price to the customer vs. the market. We would set a MAP (minimum advertised price) that was designed to deliver a significantly higher-than-average profit margin to our dealer. So, of course, the product had a price, but the focus was on dealer profit vs. end user cost. Slowly but surely, we began to see sales grow, and now twenty years later, the product line is still active, dealers are still making outstanding profits and end users have still never heard of it!!! Just how it was intended.
Slowly but surely, we began to see sales grow, and now twenty years later, the product line is still active, dealers are still making outstanding profits and end users have still never heard of it!!! Just how it was intended.


 Strategy:
Strategy:





