Visiting the JBL Experience Center
The Experience Center is located in a lovely area of LA – Northridge, CA – and was lucky enough to have escaped the recent wildfire incidents. A sprawling complex, the building is home to both the Experience Center and offices for JBL and Harman engineers, sales and marketing teams, and executives.
We arrived early in the morning and were greeted by JBL wizard David “Tewks” Tewksbury, who served as our tour guide and host for the day. After dropping our bags off in the conference room, we were escorted to the entryway of the Experience Center, which was a feast for the eyes and ears. JBL’s three Grammy awards were showcased in a long hallway which featured JBL Control 126 in-wall speakers playing some light background music. Martin LED lighting strips were programmed to dance to the music, and an AMX Varia touch panel allowed quick control of a number of preset scenes to set the mood.
 From there we were greeted with a personalized surprise – the huge Samsung video wall in the lobby had been customized to welcome the Exertis Almo team to the Experience Center!
From there we were greeted with a personalized surprise – the huge Samsung video wall in the lobby had been customized to welcome the Exertis Almo team to the Experience Center!
One of the best parts of the Experience Center…experience…is that nearly all of the Harman products on display are powered on and ready to be demonstrated. Getting the chance to play with touch panels, hear headphones, test microphones, and hear loudspeakers is not only a fantastic learning experience, but a lot of fun as well!
For example, AKG had two fantastic setups in the main lobby which were a hit with our group – a headphone demo wall and a vocal isolation booth for testing AKG microphones! The headphone demo wall had all of AKG’s studio headphones ready to demo – after donning the headphones of your choice you could select from any of eight music tracks and control volume directly from an AMX touch panel. The vocal demo booth featured AKG’s famous studio microphones – the C214, C314, and the venerable C414 XLii, and a small  Soundcraft mixer so that you could easily switch between the different models – a very enlightening experience for a mic nerd like myself!
Soundcraft mixer so that you could easily switch between the different models – a very enlightening experience for a mic nerd like myself!
Near the mic and headphone demo areas were rooms highlighting JBL’s consumer and pro-sumer home, Bluetooth, and studio products. JBL’s attractive home audio products like bookshelf speakers, turntables, headphones, PartyBoxes, and other Bluetooth speakers were set up to demo and interact with. Getting to hear the JBL 104-BT desktop monitor speakers in person was the nudge I needed to finally get a set for my work desk at home.
 But all of this was just an introduction to the main hall, where JBL loudspeakers, Crown amplifiers, BSS and dbx signal processors, AMX control and video products, and Martin lighting were on full display. Harman has put a lot of effort into this room, and they make it easy to demo, see, and A/B their installed product lineups. Tewks led us though the experience, explaining the differences between the various Crown amplifier series, discussing and demoing the multitude of JBL ceiling and wall-mounted loudspeakers and explaining fun stuff like speaker waveguides.
But all of this was just an introduction to the main hall, where JBL loudspeakers, Crown amplifiers, BSS and dbx signal processors, AMX control and video products, and Martin lighting were on full display. Harman has put a lot of effort into this room, and they make it easy to demo, see, and A/B their installed product lineups. Tewks led us though the experience, explaining the differences between the various Crown amplifier series, discussing and demoing the multitude of JBL ceiling and wall-mounted loudspeakers and explaining fun stuff like speaker waveguides.
All of this was powered by one of the prettiest AV equipment rack lineups I’ve ever seen, behind glass and beautifully lit by adjustable RGB lighting. I’ve never considered aesthetically lighting an equipment rack before, but my mind has been changed!
If all of this wasn’t enough, the highlight – by far – of our tour was getting to see and hear the brand-new audio demo room. The demo room was recently renovated and professionally acoustically treated, which was amazing to see and hear in person. The large room featured most of JBL’s compact line arrays (such as the CBT 70J-1 and CBT 1000) and outdoor all-weather speakers on one wall. We were able to hear all of these in-situ and compare their advantages and strengths. The outstanding even horizontal coverage and throw distance of these speakers has to be heard to be believed.
 On the other wall, at a relatively safe distance, were JBL’s line array speakers flown from the ceiling. The SRX, VRX, and VTX-series line array speakers are JBL’s flagship offerings for large venues, and its not everyday you get to hear this level of performance in a private setting. The folks at Harman very cleverly configured the line array demo to start at the push of a big red button – our own Brent Dowler got to do the honors. After the button was pushed, the lights went down and the show started.
On the other wall, at a relatively safe distance, were JBL’s line array speakers flown from the ceiling. The SRX, VRX, and VTX-series line array speakers are JBL’s flagship offerings for large venues, and its not everyday you get to hear this level of performance in a private setting. The folks at Harman very cleverly configured the line array demo to start at the push of a big red button – our own Brent Dowler got to do the honors. After the button was pushed, the lights went down and the show started.
Massive walls of sound – loud, but accurate, crisp, and clear – roared through the room, accompanied by a concert-level Martin lighting show, choreographed to match the music. Everything from hard rock to EDM sounded incredible. The performance literally made the hair stand up on the back of my neck!
After that experience we needed to wind down a little, so we got a chance to relax in JBL’s new Cinema Experience Room, where we got to hear JBL’s excellent range of cinema speakers in a theater-like setting. This room also housed a demo of JBL’s new Control 400 series ceiling speakers, where they could be compared to competitors’ ceiling speaker offerings.
This write-up only scratches the surface of what we got to see and hear at the JBL Experience Center; I’m running out of room and I didn’t even mention the classic JBL speaker displays, the speaker torture test rooms, and the fantastic AMX and Samsung video wall displays. My thanks to our NBT team for inviting me and to Tewks and the rest of the Harman staff for welcoming us!
If you are interested in experiencing the JBL Experience Center for yourself, reach out to me! I’d love an excuse to go back myself.

About the Author
John Rossman | CTS
BDM II – Technical Specialist
Supported Manufacturers: Harman Professional – AKG, AMX, BSS, Crown, DBX, JBL, Lexicon, Martin, & Soundcraft

 The Trade Agreements Act (TAA) was enacted to encourage fair and open international trade, but in practice it has implemented the requirement that the US government may only acquire US- or “designated end country”-made end products.
The Trade Agreements Act (TAA) was enacted to encourage fair and open international trade, but in practice it has implemented the requirement that the US government may only acquire US- or “designated end country”-made end products.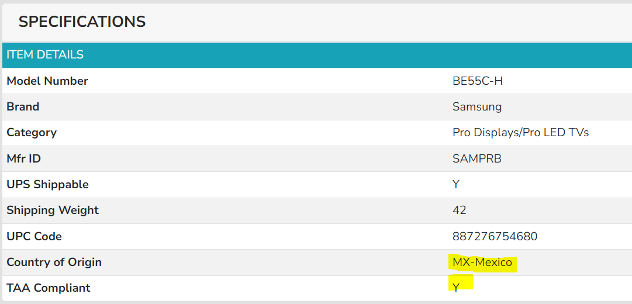

 AV OVER IP ENCODERS/DECODERS
AV OVER IP ENCODERS/DECODERS CABLES
CABLES CAMERAS
CAMERAS CONFERENCING
CONFERENCING CONTROL
CONTROL AMX
AMX  Atlas
Atlas  MOUNTS
MOUNTS DIGITAL SIGNAGE
DIGITAL SIGNAGE AMX
AMX  Here is a list of things that I don’t want to see or hear including my nicknames for each:
Here is a list of things that I don’t want to see or hear including my nicknames for each:

 In today’s interconnected world, every meeting room, collaboration space, or presentation environment demands a complete and integrated AV solution. These can be very simple or quite complex. By asking all the right questions and offering all of the best solutions accordingly—you provide customers with a reliable, user-friendly experience that meets their goals and budgets. For resellers and integrators, this approach not only drives sales but also solidifies your role as a trusted partner in delivering cutting-edge AV solutions.
In today’s interconnected world, every meeting room, collaboration space, or presentation environment demands a complete and integrated AV solution. These can be very simple or quite complex. By asking all the right questions and offering all of the best solutions accordingly—you provide customers with a reliable, user-friendly experience that meets their goals and budgets. For resellers and integrators, this approach not only drives sales but also solidifies your role as a trusted partner in delivering cutting-edge AV solutions.
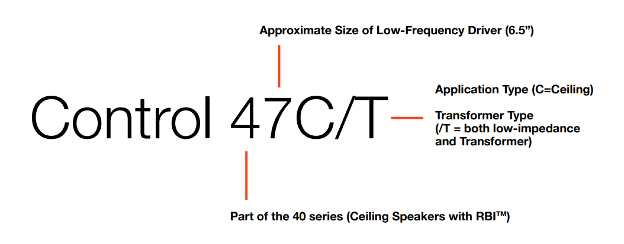
 Here we have the
Here we have the 

 Similarly, for a paging application where aesthetics are a consideration, the
Similarly, for a paging application where aesthetics are a consideration, the  Please note that despite the overlap between JBL models between various series, you should not assume that there is always an “apples-to-apples” comparison. For example, some series will have necessary accessories or features included like back cans or tile bridges, while others may not. Always research to make sure you are making the right choice, and contact us if you have questions!
Please note that despite the overlap between JBL models between various series, you should not assume that there is always an “apples-to-apples” comparison. For example, some series will have necessary accessories or features included like back cans or tile bridges, while others may not. Always research to make sure you are making the right choice, and contact us if you have questions! Does your project have any special circumstances where a typical ceiling speaker won’t work? Don’t worry – JBL has you covered!
Does your project have any special circumstances where a typical ceiling speaker won’t work? Don’t worry – JBL has you covered! Have a ceiling with limited above-ceiling clearance? Try the
Have a ceiling with limited above-ceiling clearance? Try the  Looking for a low-profile speaker which is easy to install and fits seamlessly into a standard drop-tile ceiling? Try the
Looking for a low-profile speaker which is easy to install and fits seamlessly into a standard drop-tile ceiling? Try the  What equipment is needed for a Teams meeting?
What equipment is needed for a Teams meeting? Exertis Almo offers a range of devices that meet these needs, such as the
Exertis Almo offers a range of devices that meet these needs, such as the  For example, the
For example, the  The
The 






