PanaAs the landscape of higher education evolves, so does the role of audio-visual technology in shaping learning environments for in-person and remote students. Let’s explore the top 5 trends that are revolutionizing AV in higher education institutions – and the solutions that help create a more accessible and inclusive learning space.
1. Interactive and Collaborative Learning
Interactive and engaging learning experiences are increasing in popularity among colleges and universities, and AV technology is rising to meet this demand. Interactive displays, touchscreens, and collaboration tools are transforming traditional classrooms into dynamic hubs of innovation. These spaces empower students to actively participate in their education, fostering collaboration, critical thinking, and creativity.
Projection Technology
Create engaging and collaborative learning environments with projection technology from Epson. With support for easy reading, instruction, and communication, BrightLink ensures that all students are included while bringing classrooms to life with efficient collaboration. Explore the BrightLink 760Wi Interactive Projector and the Pro 1485FI Interactive Projector for details.
 Interactive Displays
Interactive Displays
Designed to increase productivity and participation, interactive touch displays allow for effortless collaboration. Featuring a built-in camera and premium audio, Yealink’s MeetingBoard and MAXHUB’s ViewPro Series simplify classrooms and workspaces for immersive hybrid instruction.
2. Flexible Environments and Multi-Use Spaces
The shift towards flexible learning environments is reshaping the physical layout of classrooms and lecture halls in higher education. AV technology plays a crucial role in creating adaptable spaces that can easily accommodate different teaching styles and activities. Wireless presentation systems, movable furniture, and modular AV setups enable educators to customize the learning experience to meet the needs of students.
Many universities have several multi-use spaces throughout campus, and these areas require versatile technology. Higher education spaces will often use libraries for events, lecture halls for guest speakers, and cafes and study spaces for small-scale performances and entertainment.
 Audio Solutions
Audio Solutions
During lectures and events, microphone systems help amplify the presenters for better engagement from in-person and remote participants. Top of the class in education, Sennheiser’s G4 300 Series Wireless handheld base set is the best choice if you need a handheld transmitter and maximum flexibility.
[For insights into audio design for challenging multi-use spaces, check out “The Dreaded Gymcafatorium: 3 Keys to Successful Multi-Use Audio Design” with Tom Kehr.]
 Space-Saving Projection
Space-Saving Projection
Epson’s line-up of large venue projectors are an ideal choice for multi-use spaces, featuring larger-than-life images and simple installation. For rooms with limited space, the Epson laser projectors transform virtually any flat surface into a display for learning and collaboration, without taking up any space when not in use.
Portable and easy to set up in any space, Panasonic’s PT-LMW420U portable projector will help elevate communication quality with crisp, detailed images that stay clearly visible in well-lit rooms. Plus, Panasonic projectors are so intuitive they can work with the software and hardware you already have and don’t require you to be a projection expert to use them.
AV Furniture to Setup Anywhere
 AV systems must also be flexible to be able to handle constantly changing classroom needs to fit hybrid, hyflex, in-person and distance learning styles, often all in the same day. The Da-Lite Tensioned Advantage electric projection screens with SightLine elevate room aesthetics and simplify setup for flexible mounting in a variety of room sizes and ceiling heights.
AV systems must also be flexible to be able to handle constantly changing classroom needs to fit hybrid, hyflex, in-person and distance learning styles, often all in the same day. The Da-Lite Tensioned Advantage electric projection screens with SightLine elevate room aesthetics and simplify setup for flexible mounting in a variety of room sizes and ceiling heights.
Colleges and universities are embracing AV trends in digital signage now more than ever as a key element of their essential information-sharing and messaging plans for reaching everyone on campus. Whether it’s a mobile cart, floor stand, or kiosk, Legrand-AV offers the flexibility to move and place digital signage where it’s needed.
3. Assistive Listening for Inclusivity and Accessibility
 Technology that promotes inclusivity and accessibility is paramount in education spaces, as it ensures that each student has the opportunity to learn and thrive. Incorporating assistive listening technology is crucial, as it ensures that each individual can fully participate in classroom discussions and activities, fostering equal access to educational opportunities for all students.
Technology that promotes inclusivity and accessibility is paramount in education spaces, as it ensures that each student has the opportunity to learn and thrive. Incorporating assistive listening technology is crucial, as it ensures that each individual can fully participate in classroom discussions and activities, fostering equal access to educational opportunities for all students.
Perfect for venues with a capacity of up to 100 people, the the LS-57 Advanced Level II Stationary RF System from Listen Technologies broadcasts a strong, reliable RF to ensure the best possible listening experience for everyone.
4. Lecture Capture and Streaming for HyFlex Learning
In an era of digital learning, lecture capture technology has become a cornerstone of higher education institutions. AV systems equipped with lecture capture capabilities enable educators to record and archive lectures for on-demand access by students. This flexible learning model empowers students to review course materials at their own pace, reinforcing learning outcomes and accommodating diverse learning styles.
 Auto-Tracking Capabilities
Auto-Tracking Capabilities
Engineered to simplify the hybrid learning process, auto-tracking cameras are a great option to ensure that students can always see the professor during the lecture. The Move 4K is the latest PTZ camera from PTZOptics, featuring auto-tracking for a more intelligent video production workflow. The Move 4K is capable of 4K at 60fps (1080p at 60fps over SDI), future-proofing your technology investment while still accommodating HD and Full HD video resolution equipment.
Lecture-Capture Solutions for the Classroom
In modern classrooms, lecture capture is essential to create an inclusive learning experience for each student. Additionally, many courses are now asynchronous, requiring a professor to pre-record the lecture material and upload for the students’ review.
 Panasonic’s LCS-100 lecture capture appliance integrates with the ATS-200 / ATS-400 auto-tracking servers, and PTZ cameras with voice-triggered presets using Panasonic Pro Audio, including ceiling microphones, gooseneck and boundary microphones, and more.
Panasonic’s LCS-100 lecture capture appliance integrates with the ATS-200 / ATS-400 auto-tracking servers, and PTZ cameras with voice-triggered presets using Panasonic Pro Audio, including ceiling microphones, gooseneck and boundary microphones, and more.
The LC200 CaptureVision System from Lumens is an all-in-one media station that allows instructors to easily mix video and audio sources while streaming and recording lectures for engaging and attractive presentations.
5. AI-Powered Tech and Data for a Personalized Experience
 Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are reshaping the landscape of higher education by enabling personalized learning experiences for each student. AI-powered analytics tools analyze student data to identify learning patterns, preferences, and areas for improvement. With this insight, educators can tailor instruction to meet the unique needs of each student, fostering deeper engagement and academic success. Here are a few key solutions to create a personalized experience for students:
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are reshaping the landscape of higher education by enabling personalized learning experiences for each student. AI-powered analytics tools analyze student data to identify learning patterns, preferences, and areas for improvement. With this insight, educators can tailor instruction to meet the unique needs of each student, fostering deeper engagement and academic success. Here are a few key solutions to create a personalized experience for students:
AVer’s VB130 is a powerful, all-in-one hybrid learning tool featuring 4K video and built-in audio for an exceptional student experience. With advanced AI and SmartFrame technology, the videobar keeps the professor in camera view while focusing on their voice so students do not miss any content.
Designed for remote teaching rooms, Yealink’s A20 + CTP18 is equipped with AI technology, including auto-framing and speaker tracking, allowing instructors to create a vivid classroom experience without restricting movement.
Summing It Up
The future of higher education is bright with possibilities, thanks to the transformative power of audio-visual technology. As institutions continue to embrace these solutions and trends, we’re excited to partner with you in delivering innovative products that elevate learning experiences and empower students in the classroom and online.
Ready to embark on your AV journey?
Reach out to us today to explore how Exertis Almo can help you harness the power of technology to transform your educational projects.
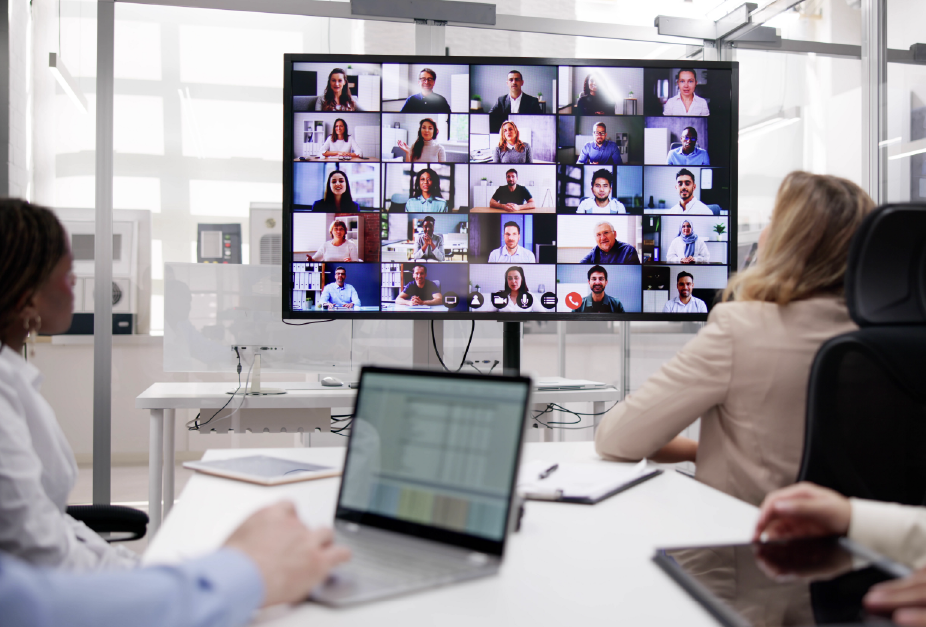 Optimizing Collaboration Spaces for Hybrid Work
Optimizing Collaboration Spaces for Hybrid Work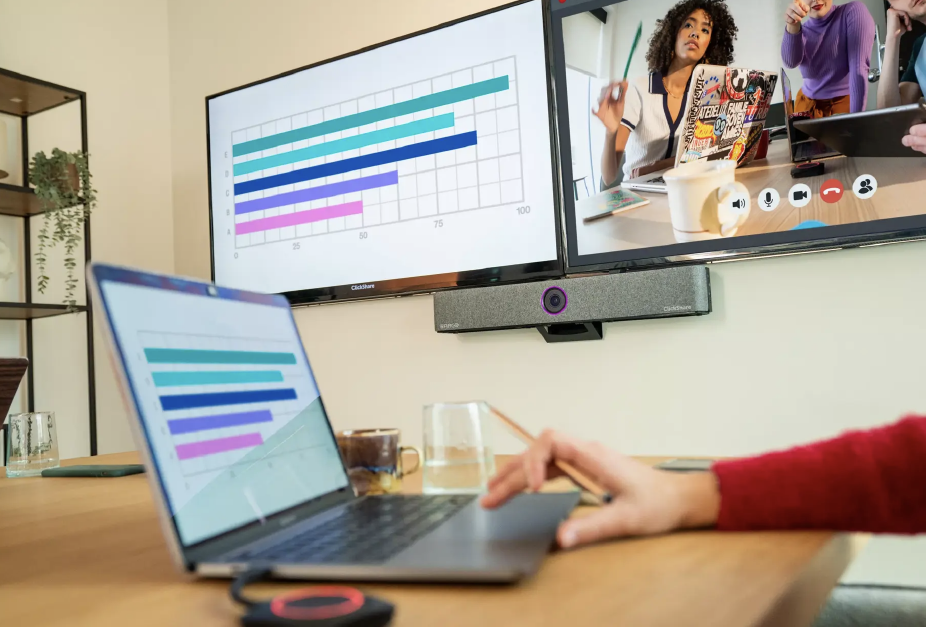 At the forefront of these trends stands the Barco all-in-one ClickShare Bar, Core and Pro models – a compact, yet powerful solution designed to elevate collaboration spaces to new heights. Combining wireless content sharing, conference camera, microphone, and speaker functionalities into a single device, the Barco all-in-one bar offers unparalleled convenience and versatility. Ideal for spaces up to 15’ x 15’, this innovative solution simplifies meeting room setups while delivering exceptional audio and video quality.
At the forefront of these trends stands the Barco all-in-one ClickShare Bar, Core and Pro models – a compact, yet powerful solution designed to elevate collaboration spaces to new heights. Combining wireless content sharing, conference camera, microphone, and speaker functionalities into a single device, the Barco all-in-one bar offers unparalleled convenience and versatility. Ideal for spaces up to 15’ x 15’, this innovative solution simplifies meeting room setups while delivering exceptional audio and video quality.

 1. Digital Menu Boards for Dynamic Displays
1. Digital Menu Boards for Dynamic Displays Gone are the days of crackling speakers and static-filled orders. AV technology is revolutionizing the drive-thru ordering experience, providing crystal-clear audio and seamless communication between customers and staff. Peerless-AV’s
Gone are the days of crackling speakers and static-filled orders. AV technology is revolutionizing the drive-thru ordering experience, providing crystal-clear audio and seamless communication between customers and staff. Peerless-AV’s  For those who choose to order in-store, interactive ordering kiosks empower customers to take control of their ordering experience. These user-friendly touchscreens provide a convenient way for patrons to browse menus, customize orders, and complete transactions independently. By streamlining the ordering process, QSRs can reduce wait times, minimize order errors, and improve overall operational efficiency.
For those who choose to order in-store, interactive ordering kiosks empower customers to take control of their ordering experience. These user-friendly touchscreens provide a convenient way for patrons to browse menus, customize orders, and complete transactions independently. By streamlining the ordering process, QSRs can reduce wait times, minimize order errors, and improve overall operational efficiency. The
The 
 As detailed in the blog, “
As detailed in the blog, “

 Space-Saving Projection
Space-Saving Projection AV systems must also be flexible to be able to handle constantly changing classroom needs to fit hybrid, hyflex, in-person and distance learning styles, often all in the same day. The Da-Lite
AV systems must also be flexible to be able to handle constantly changing classroom needs to fit hybrid, hyflex, in-person and distance learning styles, often all in the same day. The Da-Lite  Technology that promotes inclusivity and accessibility is paramount in education spaces, as it ensures that each student has the opportunity to learn and thrive. Incorporating assistive listening technology is crucial, as it ensures that each individual can fully participate in classroom discussions and activities, fostering equal access to educational opportunities for all students.
Technology that promotes inclusivity and accessibility is paramount in education spaces, as it ensures that each student has the opportunity to learn and thrive. Incorporating assistive listening technology is crucial, as it ensures that each individual can fully participate in classroom discussions and activities, fostering equal access to educational opportunities for all students.
 Panasonic’s LCS-100 lecture capture appliance integrates with the ATS-200 / ATS-400 auto-tracking servers, and
Panasonic’s LCS-100 lecture capture appliance integrates with the ATS-200 / ATS-400 auto-tracking servers, and 

 2. Creating a Roadmap:
2. Creating a Roadmap: It would seem to make sense then that we should be designing the room, and the meeting environment, first around the human and then applying the appropriate technology within the boundaries of human factors and ergonomics.
It would seem to make sense then that we should be designing the room, and the meeting environment, first around the human and then applying the appropriate technology within the boundaries of human factors and ergonomics. A close second to the maximum allowable background noise level is the acoustical performance of the space. This is the actual sound signature of the room, and I can think of nothing more important that is also the least considered or even ignored. While the trend has been towards glass walls, shiny floors, wood panels and other acoustically “hard” surfaces, these materials are the least friendly when it comes to the acoustical criteria needed for human communication. Jun Lim recently wrote, “No matter how excellent an audio system is, it cannot surpass the limitations imposed by the acoustic environment.” The late John Murray once said, “Once the sound leaves the loudspeakers, it’s out in the wild”. “Acoustically friendly” doesn’t have to mean plain or ugly but aesthetics devoid of acoustical considerations impedes the ability to communicate.
A close second to the maximum allowable background noise level is the acoustical performance of the space. This is the actual sound signature of the room, and I can think of nothing more important that is also the least considered or even ignored. While the trend has been towards glass walls, shiny floors, wood panels and other acoustically “hard” surfaces, these materials are the least friendly when it comes to the acoustical criteria needed for human communication. Jun Lim recently wrote, “No matter how excellent an audio system is, it cannot surpass the limitations imposed by the acoustic environment.” The late John Murray once said, “Once the sound leaves the loudspeakers, it’s out in the wild”. “Acoustically friendly” doesn’t have to mean plain or ugly but aesthetics devoid of acoustical considerations impedes the ability to communicate.

 Being that I am now 42 years old and have worked in Telecom and AV for the better part of 2 decades, I have 12+ trips to Las Vegas completed and feel like I know what to expect each time I fly into Harry Reid International Airport. First, it was the annual DIRECTV Revolution Conference, then it was Channel Partners, followed by InfoComm in alternating years. As I have explained to my wife (who has never been), I feel like the mystique of Las Vegas wears off after the first or second trip out there. However, when I was approached back in 2019 with the chance to attend my first ever JBL Fest, I felt the type of excitement as if I had never been there and was eager to experience a new list of firsts. Unfortunately, a family health scare cancelled my trip that year and 2 years-worth of a Pandemic further delayed my first JBL Fest until 2022. Having enjoyed last year as much as I did, I still felt a certain sense of the “exciting unknown” when I was invited to attend again this year. Along with our Exertis Almo Incentive Winners – Josh Taylor, Kyle Smith, Randy Robinovitch, and Ray Farler, I headed out to Las Vegas and made sure to document JBL Fest 2023 for all of you!
Being that I am now 42 years old and have worked in Telecom and AV for the better part of 2 decades, I have 12+ trips to Las Vegas completed and feel like I know what to expect each time I fly into Harry Reid International Airport. First, it was the annual DIRECTV Revolution Conference, then it was Channel Partners, followed by InfoComm in alternating years. As I have explained to my wife (who has never been), I feel like the mystique of Las Vegas wears off after the first or second trip out there. However, when I was approached back in 2019 with the chance to attend my first ever JBL Fest, I felt the type of excitement as if I had never been there and was eager to experience a new list of firsts. Unfortunately, a family health scare cancelled my trip that year and 2 years-worth of a Pandemic further delayed my first JBL Fest until 2022. Having enjoyed last year as much as I did, I still felt a certain sense of the “exciting unknown” when I was invited to attend again this year. Along with our Exertis Almo Incentive Winners – Josh Taylor, Kyle Smith, Randy Robinovitch, and Ray Farler, I headed out to Las Vegas and made sure to document JBL Fest 2023 for all of you! Landing Las Vegas, you are almost immediately greeted by hosts holding “JBL Fest” signage at the baggage claim area and are ushered to a waiting shuttle (aka a rather swanky party bus) which took us to the Park MGM where we would be staying for the next 2 days. Surprise #1 on this trip was while I was checking in and I lift my head to notice Kevin Humphrey, Harman Distribution Manager (and close friend), standing next to me. I have always said that I am only as successful as those around me, so to be able to share this experience with someone deserving like Kevin made the event that much more rewarding. We then walked to the Hospitality Suite where I received a welcome packet and the “infamous” JBL Fest Swag Bag. This year, the bag contained several JBL branded items such as water bottles and hand sanitizer, but the highlight was the customized pair of JBL Tour Pro 2 earbuds. If you are not familiar with these, they are JBL’s newest noise cancelling earbuds which were featured in WIRED’s Best of CES 2023. Spatial Audio, wireless charging, and a first of its kind touch display on the charging case make these anything but your typical earbuds. I had to open and pair them with my phone the second I got to my room! Once we got to the complimentary lunch, I was able to meet with our team as well as with Frank Joseph and Whitney Bosch from the Harman marketing team as we game-planned the day and discussed all that was happening.
Landing Las Vegas, you are almost immediately greeted by hosts holding “JBL Fest” signage at the baggage claim area and are ushered to a waiting shuttle (aka a rather swanky party bus) which took us to the Park MGM where we would be staying for the next 2 days. Surprise #1 on this trip was while I was checking in and I lift my head to notice Kevin Humphrey, Harman Distribution Manager (and close friend), standing next to me. I have always said that I am only as successful as those around me, so to be able to share this experience with someone deserving like Kevin made the event that much more rewarding. We then walked to the Hospitality Suite where I received a welcome packet and the “infamous” JBL Fest Swag Bag. This year, the bag contained several JBL branded items such as water bottles and hand sanitizer, but the highlight was the customized pair of JBL Tour Pro 2 earbuds. If you are not familiar with these, they are JBL’s newest noise cancelling earbuds which were featured in WIRED’s Best of CES 2023. Spatial Audio, wireless charging, and a first of its kind touch display on the charging case make these anything but your typical earbuds. I had to open and pair them with my phone the second I got to my room! Once we got to the complimentary lunch, I was able to meet with our team as well as with Frank Joseph and Whitney Bosch from the Harman marketing team as we game-planned the day and discussed all that was happening. Next stop was a VIP-access tour of Allegiant Stadium which is where the Las Vegas Raiders play their home games. Seeing as how I just recently took my daughter on a tour of Citizens Bank Park as well as Lincoln Financial Field, this was right up my alley! Aside from going down to the field level and experiencing this newer facility up close, we received some behind the scenes sneak peaks into the A/V which included their control/IT room which housed an impressive 50+ Crown DCI4x1250N amplifiers and multiple BSS Processors amongst other items. Simply standing next to the rack of amps was eye-opening as you realize how much it takes to truly power that type of operation. While we didn’t get up close to the speakers, we did learn it was the JBL VLA Series of Line Array Speakers which are typically found in stadium-type applications. Following the tour we had a little downtime before meeting up for the evening welcoming reception at the Hotel, which we were greeted by a team photo opportunity and another swag bag complete with a custom JBL Fest Masterclass Bluetooth speaker. This opening event was followed by an even bigger party at the onsite club. Mingling with a diverse group of worldwide influencers and Harman executives is always fun but I was fortunate enough to make my way to the Harman VIP lounge which then led to a once in a lifetime opportunity! Kyle Smith and I were invited into a back room where we met and had a photo opportunity with Lenny Kravitz! To finish things off was a rather surprise appearance from Grammy winning artist Bruno Mars who sang along with some of his biggest hits. Not a bad way to spend a Thursday night!
Next stop was a VIP-access tour of Allegiant Stadium which is where the Las Vegas Raiders play their home games. Seeing as how I just recently took my daughter on a tour of Citizens Bank Park as well as Lincoln Financial Field, this was right up my alley! Aside from going down to the field level and experiencing this newer facility up close, we received some behind the scenes sneak peaks into the A/V which included their control/IT room which housed an impressive 50+ Crown DCI4x1250N amplifiers and multiple BSS Processors amongst other items. Simply standing next to the rack of amps was eye-opening as you realize how much it takes to truly power that type of operation. While we didn’t get up close to the speakers, we did learn it was the JBL VLA Series of Line Array Speakers which are typically found in stadium-type applications. Following the tour we had a little downtime before meeting up for the evening welcoming reception at the Hotel, which we were greeted by a team photo opportunity and another swag bag complete with a custom JBL Fest Masterclass Bluetooth speaker. This opening event was followed by an even bigger party at the onsite club. Mingling with a diverse group of worldwide influencers and Harman executives is always fun but I was fortunate enough to make my way to the Harman VIP lounge which then led to a once in a lifetime opportunity! Kyle Smith and I were invited into a back room where we met and had a photo opportunity with Lenny Kravitz! To finish things off was a rather surprise appearance from Grammy winning artist Bruno Mars who sang along with some of his biggest hits. Not a bad way to spend a Thursday night!
 Waking up on Friday I knew we were in for a long but rewarding day. First off was breakfast which came complete with a Johnny Fly Sunglasses gifting station! You essentially walk up and try on several pairs of high-end sunglasses and then say “ok ill take these”. The wrap them up in a custom JBL case and you are on your way! We then made our way to the Installed Audio Masterclass presented by
Waking up on Friday I knew we were in for a long but rewarding day. First off was breakfast which came complete with a Johnny Fly Sunglasses gifting station! You essentially walk up and try on several pairs of high-end sunglasses and then say “ok ill take these”. The wrap them up in a custom JBL case and you are on your way! We then made our way to the Installed Audio Masterclass presented by 
 We immediately went to the JBL Stage with VIP access where we all met up for drinks, food, and music. I ventured off while Bebe Rexha was performing and found myself with perfect view of the main stage where an EDM DJ was getting the crowd fired up for the next act. After looking through the street vendors and other areas, I called it a night as I listened to Bebe Rexha perform with special guest Tyler Hubbard (from Florida Georgia Line). The Killers were the headliner of Friday night and through videos I saw from Josh Taylor, it seemed our entire team left the trip on a high note!
We immediately went to the JBL Stage with VIP access where we all met up for drinks, food, and music. I ventured off while Bebe Rexha was performing and found myself with perfect view of the main stage where an EDM DJ was getting the crowd fired up for the next act. After looking through the street vendors and other areas, I called it a night as I listened to Bebe Rexha perform with special guest Tyler Hubbard (from Florida Georgia Line). The Killers were the headliner of Friday night and through videos I saw from Josh Taylor, it seemed our entire team left the trip on a high note!





